
In the world of cosmetics products, oils serve as essential raw materials that play a pivotal role in enhancing appearance, texture, stability, and efficacy. Oils, including types like essential oils, s, and greases, are integral to various skin care products, personal care products, and even cosmetic decisions such as plastic packaging and bottles. But what specific types of oils are commonly used in cosmetic formulations, and what functions do they perform?

Grease and oil in cosmetics are derived from fatty acid glycerides created by combining fatty acids with glycerol. These include mono-, di-, and triglycerides, and their variations result in a wide range of cosmetic oils. For simplicity, these types of oil are often grouped into two main classifications:
State at Room Temperature: Oils can be categorized as solid, liquid, or semi-solid, which affects the texture and feel of cosmetics products.
Source: Oils are sourced from mineral, vegetable, animal, or synthetically created options, each with distinct advantages and functions in formulations.
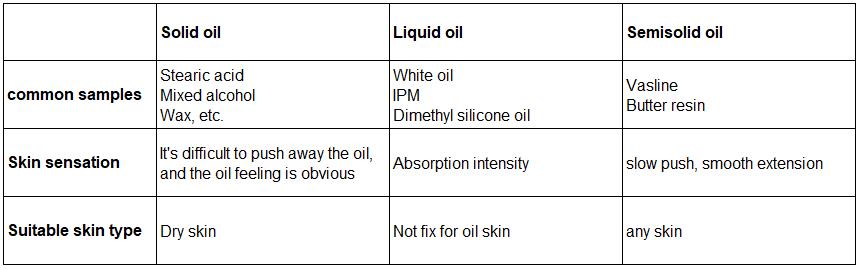
The use of oils across skin care products, serums, body s, and makeup formulations is critical to meet the growing demand for skin hydration, balance, and texture enhancement. Here are the eight primary functions of oils in cosmetics products:
Moisturizing: Providing moisture is one of the essential functions of oils in personal care products. Oils like mineral oil and jojoba oil serve as skin moisturizers, making the skin soft, smooth, and supple.
Barrier Formation: Solid and semi-solid oils create a protective barrier on the skin, preventing moisture loss and offering protection from external irritants. These oils are particularly useful in s and lotions meant for dry skin.
Cleansing: Oils in products such as makeup removers help dissolve oily residue and impurities, making them easier to remove from the skin due to the “like dissolves like” principle.
Solvent Properties: Oils like isoparaffins are often used in formulations as solvents to blend other ingredients. These solvent oils are widely found in cosmetics ranging from color cosmetics to creams, hand lotions, and even hair care products.
Emulsification: In the world of cosmetic raw materials, certain oils act as emulsifiers that enable water and oil to mix, creating smooth, consistent textures. Typical emulsifying oils include polysorbate-60 and glycerol stearate.
Texture Modification: Oils like carnauba wax and candela wax are used in products like hair waxes and mascaras to add texture and structure, creating a specific look and feel.
Enhancing Skin Feel: Cosmetic formulators carefully select oils to adjust how a product feels on the skin. For instance, facial massage creams often combine mineral oil with lighter oils to reduce heaviness and enhance freshness.
Carrier Function: Oils act as carriers for active ingredients, aiding in their delivery and absorption by the skin. For example, phospholipid complexes and liposome encapsulation technology utilize oils as carriers to enhance the efficacy of active ingredients.
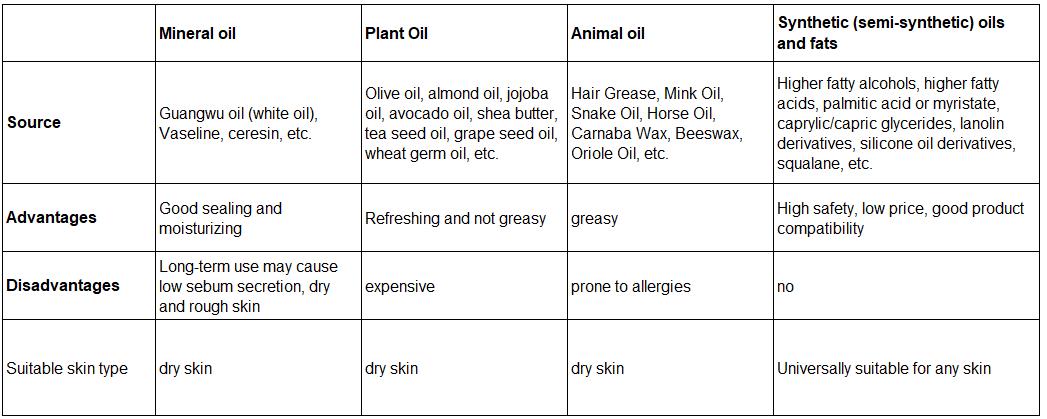
Oils used in cosmetics are evaluated based on specific physicochemical standards to ensure product safety and effectiveness. Key quality parameters include:
Acid Value: Generally less than 1, indicating a low level of acidity.
Saponification Value: Typically between 180 and 200, ensuring that oils can blend effectively in formulations.
Iodine Value: This determines the drying properties of oils. Non-drying oils have a value below 100, while drying oils have a value above 130.

Additionally, cosmetic oils must adhere to regulations like those in the 2021 Catalogue of Used Cosmetic Raw Materials and meet the standards outlined in the Technical Specifications for the Safety of Cosmetics (2015) for factors such as microbial safety and heavy metal content.
Understanding the "oil" family in cosmetics—from moisturizers and cleansing oils to emulsifiers and active ingredient carriers—sheds light on how these ingredients create effective and pleasurable experiences in cosmetics and personal care products.






